EX-99.1
Published on October 25, 2022
Exhibit 99.1
KVH Inertial Navigation Segment
Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020
and the six months ended June 30, 2022 (unaudited) and 2021 (unaudited)
1

2

3
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands)
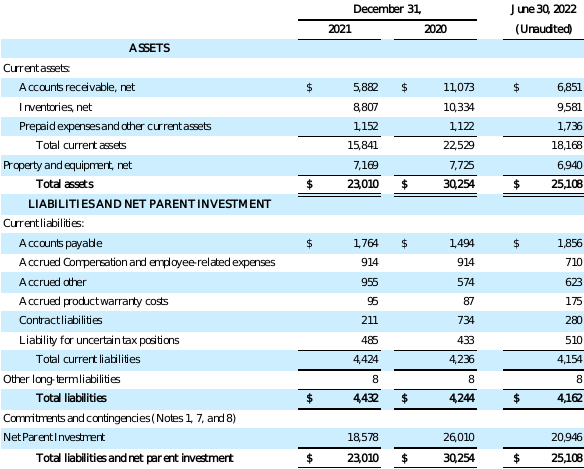
4
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND CHANGES IN NET PARENT INVESTMENT
(in thousands)
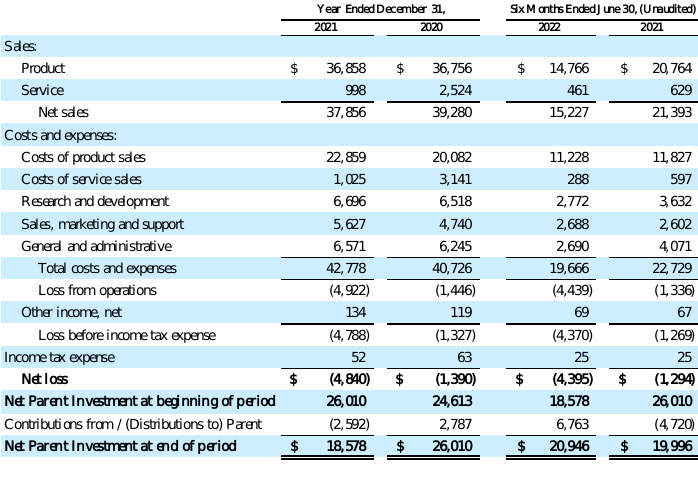
5
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
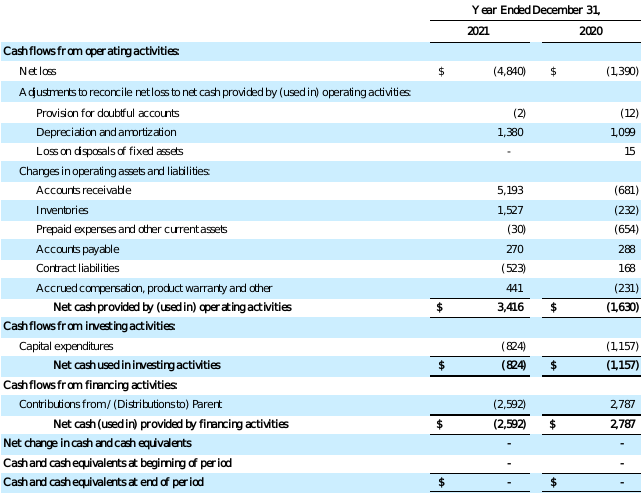
See accompanying Notes to Financial Statements.
6
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
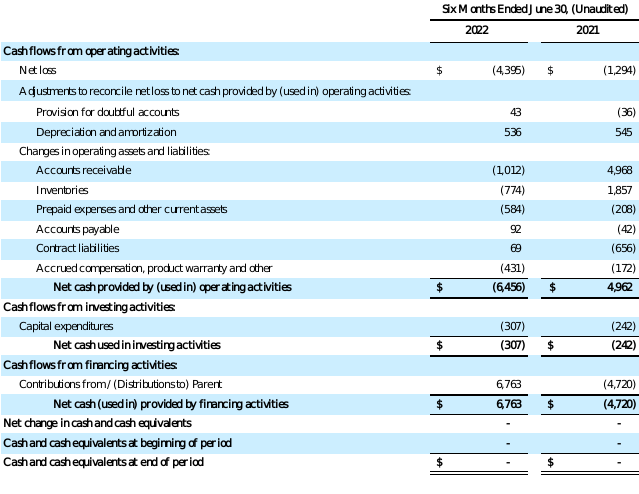
See accompanying Notes to Financial Statements.
7
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(in thousands)
(1)Description of Business
The KVH Inertial Navigation Segment (the “IN Segment”) designs, develops, manufactures and markets products for both the commercial and defense markets. Until the date of its sale (see Note 9), the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment business was 100% controlled by KVH Industries, Inc (the “Company”).
Inertial Navigation products offer precision fiber optic gyro (FOG)-based systems that enable platform and optical stabilization, navigation, pointing and guidance. Inertial Navigation products also include tactical navigation systems that provide uninterrupted access to navigation and pointing information in a variety of military vehicles, including tactical trucks and light armored vehicles. Inertial Navigation products are sold directly to U.S. and foreign governments and government contractors, as well as through an international network of authorized independent sales representatives. In addition, Inertial Navigation technology is used in numerous commercial products, such as navigation and positioning systems for various applications including autonomous platforms, precision mapping, dynamic surveying, train location control and track geometry measurement systems, industrial robotics and optical stabilization.
Inertial Navigation service sales include product repairs, engineering services provided under development contracts and extended warranty sales.
(2)Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
a)Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements and related notes of the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment are presented on a carve-out basis and have been prepared from the historical consolidated balance sheets, statements of operations and cash flows attributed to the inertial navigation business of KVH Industries, Inc. and in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (U.S. GAAP). Historically, financial statements of KVH Industries, Inc’s inertial navigation business have not been prepared as it has not operated separately from KVH Industries, Inc. These financial statements reflect the revenues and direct expenses of KVH Industries, Inc’s inertial navigation business and include material assets and liabilities of KVH Industries, Inc. that are specifically identifiable to the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment. Additionally, the financial statements include an allocation of indirect expenses of KVH Industries, Inc. related to managing the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment and operating its business including salaries, equity-based compensation and other general and administrative expenses based on an estimate of expenses had the inertial navigation business been run as an independent entity. This allocation method is principally based on revenue for corporate sales and marketing expenses as well as general and administrative expenses, and principally based on activity for research and development expenses. Actual results may differ from these allocations, assumptions and estimates. Management believes the assumptions underlying its allocation of indirect expenses are reasonable. For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment was allocated $2,076 and $1,825, respectively, of salaries, other compensation, and corporate marketing, and $6,571 and $6,245, respectively, of other general and administrative expenses. For the six months ending June 30, 2022 and 2021, the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment was allocated $1,012 (unaudited) and $1,119 (unaudited), respectively, of salaries, other compensation, and corporate marketing, and $2,690 (unaudited) and $4,071 (unaudited), respectively, of other general and administrative expenses.
8
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
Actual costs that would have been incurred if the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment had been a standalone company would depend on multiple factors, including organization structure and strategic decisions made in various areas. Consequently, future results of operations will include costs and expenses that may be materially different than historical results of operations. Accordingly, the financial statements included herein are not indicative of the future results of operations, financial position and cash flows.
The net parent investment consists of: (1) financing the carved-out inertial navigation business received from the Company to fund its operations through contributions to the inertial navigation business that did not require repayments, (2) the net effect of cost allocations from transactions with the Company, and (3) the inertial navigation business’ accumulated earnings. In order to record the cost allocation, a corresponding entry is made to the net parent investment account, since such amounts are expected to be settled through an equity contribution rather than cash paid by the inertial navigation business to the Company.
The KVH Inertial Navigation Segment is party to a centralized cash management arrangement which requires management to make determinations about the presentation in the IN Segment’s balance sheet of any amounts resulting from participation in the cash pool. As the IN Segment is not required to make repayments to the Company under the cash management arrangement, management has determined that it is appropriate to report the effects of transactions with the cash pool arrangement within equity as part of the parent’s net investment and to classify the transactions in the IN Segment’s statements of cash flows as financing activities.
The financial statements have been presented assuming the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment operates as a going concern. The operations of the inertial navigation business are dependent upon the Company’s support such that all cash flows used in its operating and investing activities have been funded through the Company’s equity contributions. The IN Segment’s ability to continue as a going concern depends on such ongoing support. The Company and the recent acquirer of the IN Segment (see Note 9) have committed to providing this ongoing support through equity contributions as required to fund operations
The Company has prepared the accompanying unaudited interim financial statements and notes in conformity with US GAAP for interim financial information. Accordingly, they do not include all of the information and disclosures required by US GAAP for complete financial statements. In the opinion of the Company’s management, the accompanying interim financial statements reflect all adjustments, which include normal recurring adjustments, necessary to present fairly the Company’s interim financial information.
The financial results for any interim period are not necessarily indicative of the expected financial results for the full year.
b)Significant Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of sales and expenses during the reporting periods.
Although the Company regularly assesses these estimates, actual results could differ materially from these estimates. Changes in estimates are recorded in the period in which they become known. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience and various other assumptions that it believes to be reasonable under the circumstances.
9
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
c)Trade Accounts Receivable
Although the Company does not foresee that credit risk associated with trade accounts receivables will deviate from historical experience, repayment is dependent upon the financial stability of individual customers. The Company establishes allowances for potential bad debts and evaluates, on a monthly basis, the adequacy of those reserves based upon historical experience and its expectations for future collectability concerns. The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of the financial condition of its customers and generally does not require collateral. Activity within the Company’s allowance for doubtful accounts for the periods presented is as follows:
December 31, |
June 30, 2022 (Unaudited) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2021 |
2020 | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ 41 | $ 53 | $ 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additions (subtractions) | 28 | (75) | 42 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deductions (write-offs/recoveries) from reserve | (30) | 63 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance | $ 39 | $ 41 | $ 82 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
d)Revenue Recognition
In accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606, revenue is recognized when a customer obtains control of promised products and services. The amount of revenue recognized reflects the consideration which the Company expects to be entitled to receive in exchange for these products and services. To achieve this core principle, the Company applies the following five steps:
1) Identify the contract with a customer
A contract with a customer exists when (i) the Company enters into an enforceable contract with a customer that defines each party’s rights regarding the products and services to be transferred and identifies the payment terms related to these products and services, (ii) the contract has commercial substance, and (iii) the Company determines that collection of substantially all consideration for products and services that are transferred is probable based on the customer’s intent and ability to pay the promised consideration. The Company applies judgment in determining the customer’s ability and intention to pay, which is based on a variety of factors, including the customer’s historical payment pattern or, in the case of a new customer, published credit and financial information pertaining to the customer.
2) Identify the performance obligations in the contract
Performance obligations promised in a contract are identified based on the products and services that will be transferred to the customer that are both capable of being distinct, whereby the customer can benefit from the product or service either on its own or together with other resources that are readily available from third parties or from the Company, and are distinct in the context of the contract, whereby the transfer of the product or service is separately identifiable from other promises in the contract. To the extent a contract includes multiple promised products and services, the Company must apply judgment to determine whether promised products and services are capable of being distinct and distinct in the context of the contract. If these criteria are not met, the promised products and services are accounted for as a combined performance obligation.
10
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
3) Determine the transaction price
The transaction price is determined based on the consideration to which the Company will be entitled in exchange for transferring products and services to the customer. To the extent the transaction price includes variable consideration, the Company estimates the amount of variable consideration that should be included in the transaction price utilizing either the expected value method or the most likely amount method, depending on the nature of the variable consideration. Variable consideration is included in the transaction price if, in the Company’s judgment, it is probable that a significant future reversal of cumulative revenue under the contract will not occur.
4) Allocate the transaction price to performance obligations in the contract
If the contract contains a single performance obligation, the entire transaction price is allocated to the single performance obligation. However, if a series of distinct products or services that are substantially the same qualify as a single performance obligation in a contract with variable consideration, the Company must determine if the variable consideration is attributable to the entire contract or to a specific part of the contract. Contracts that contain multiple performance obligations require an allocation of the transaction price to each performance obligation based on a relative standalone selling price basis unless the transaction price is variable and meets the criteria to be allocated entirely to a performance obligation or to a distinct product or service that forms part of a single performance obligation. The Company determines standalone selling price based on the price at which the performance obligation is sold separately. If the standalone selling price is not observable through past transactions, the Company estimates the standalone selling price taking into account available information such as market conditions and internally approved pricing guidelines related to the performance obligations.
5) Recognize revenue when or as the Company satisfies a performance obligation
The Company satisfies performance obligations either over time or at a point in time. Revenue is recognized at the time the related performance obligation is satisfied by transferring a promised product or service to a customer.
Inertial navigation product sales
Revenue from product sales is recognized when control of the goods is transferred to the customer, which generally occurs at the Company’s plant or warehouse upon delivery to the carrier for shipment. Revenue related to shipping and handling is recognized when the products are shipped and the associated costs are accrued for based on the Company’s election to account for shipping and handling activities as a fulfillment of the promise to transfer the products and not as a combined promise.
For certain product sales, customer acceptance or inspection may be required before control of the goods is transferred to the customer. For those sales, revenue is recognized after notification of customer acceptance and the goods have been delivered to the carrier for shipment. In certain circumstances customers may request a bill-and-hold arrangement. Under these bill-and-hold arrangements, revenue is recognized when the Company has fulfilled all of its performance obligations, the customer has obtained control and substantially all of the benefits of ownership have transferred.
Standard payment terms for product sales are generally Net 30. Under certain limited conditions, the Company, at its sole discretion, provides for the return of goods. No product is accepted for return and no credit is allowed on any returned product unless management has granted and confirmed prior written permission by means of appropriate authorization. The Company establishes reserves for potential sales returns, credits, and allowances, and evaluates, on a monthly basis, the adequacy of those reserves based upon historical experience and expectations for the future.
11
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
Inertial navigation service sales
The Company engages in contracts for development, production, and services activities related to standard product modification or enhancement. The Company considers the nature of these contracts and the types of products and services provided when determining the proper accounting for a particular contract. Customer and government-agency contracted engineering service and sales under development contracts are recognized primarily during the periods in which the Company performs the service or development efforts in accordance with the agreement. Services performed under these types of contracts include engineering studies, surveys, building construction, prototype development, and program management. Performance is determined principally by comparing the accumulated labor hours incurred to date with management’s estimate of the total labor hours to complete the contracted work. Incurred labor hours represent work performed, which corresponds with and best depicts the transfer of control to the customer. This continuous transfer of control to the customer is supported by clauses in the contract that allow the customer to unilaterally terminate the contract for convenience, pay the Company for costs incurred plus a reasonable profit and take control of any work in process. The Company establishes billing terms at the time project deliverables and milestones are agreed. Unbilled revenue recognized in excess of the amounts invoiced to clients are classified within the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as “accounts receivable” as the Company's right to consideration is unconditional.
Inertial navigation product service sales
Product service sales other than under development contracts are recognized when completed services are delivered to the customer. The Company also sells extended warranty. Sales under these contracts are recognized ratably over the contract term. Product service sales including extended warranties are not a significant portion of the Company’s service sales.
e)Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying amounts of the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment’s financial instruments, which include accounts receivable and accounts payable, approximate their fair values due to the short maturity of these instruments.
f)Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost and net realizable value using the first-in first-out costing method. The Company adjusts the carrying value of KVH Inertial Navigation Segment inventory based on the consideration of excess and obsolete components based on future estimates of demand and records inventory charges to costs of product sales.
g)Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is computed on the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets. The principal lives used in determining the depreciation rates of various assets are: buildings and improvements, 5-40 years; machinery and equipment, 4-10 years; and office and computer equipment, 3-7 years.
12
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
h)Product Warranty
KVH Inertial Navigation Segment products carry standard limited warranties that range from one to two years and vary by product. The warranty period begins on the date of purchase. The Company accrues estimated product warranty costs at the time of sale and any additional amounts are recorded when such costs are probable and can be reasonably estimated. Factors that affect the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment’s warranty liability include the number of units sold, historical and anticipated rates of warranty repairs and the cost per repair. Warranty and related costs are reflected within sales, marketing and support in the accompanying statements of operations and changes in net parent investment. The following table summarizes product warranty activity:
December 31, |
June 30, 2022 (Unaudited) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2021 |
2020 | (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ 87 | $ 437 | $ 95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charges to expense | 57 | 15 | 110 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Costs incurred | (49) | (365) | (30) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance | $ 95 | $ 87 | $ 175 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
i)Shipping and Handling Costs
Shipping and handling costs are expensed as incurred and included in cost of sales. Billings for shipping and handling are reflected within net sales in the accompanying statements of operations and changes in net parent investment.
j)Research and Development
Expenditures for research and development, including customer-funded research and development, are expensed as incurred. Revenue and related development costs from customer-funded research and development are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, (Unaudited) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2022 | 2021 | |||||||||||||||||
| Customer-funded service sales | $ 363 | $ 2,063 | $ 146 | $ 291 | ||||||||||||||||
| Customer-funded costs included in costs of service sales | $ 803 | $ 2,935 | $ 70 | $ 489 | ||||||||||||||||
k)Advertising Costs
Costs related to advertising are expensed as incurred. Advertising expense was $128 and $171 for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively and for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 amounted to $44 (unaudited) and $75 (unaudited), respectively, and is included in sales, marketing, and support expense in the accompanying statements of operations and changes in net parent investment.
13
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
l)Income Taxes
KVH Industries, Inc. is subject to income taxes in the U.S. and in numerous foreign jurisdictions and accounts for income taxes following ASC Topic 740, Accounting for Income Taxes. Although the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment has not filed income taxes separately, for the purposes of these financial statements, management has performed an analysis to determine the various tax attributes that relate to the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment and has estimated what the tax liability would be if the segment had operated as a stand-alone tax filer.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that some or all of a deferred tax asset will not be realized. The Company determines whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination. If it is not more likely than not that a position will be sustained, no amount of the benefit attributable to the position is recognized. The tax benefit to be recognized of any tax position that meets the more likely than not recognition threshold is calculated as the largest amount that is more than 50% likely of being realized upon resolution of the contingency.
The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. See Note 5 for further discussion of income taxes.
m)Contingent Liabilities
KVH Industries, Inc. estimates the amount of potential exposure it may have with respect to claims, assessments and litigation in accordance with ASC 450, Contingencies.
(3) Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost and net realizable value using the first-in first-out costing method. Inventories as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and June 30, 2022 include the costs of material, labor, and factory overhead. Components of inventories consist of the following:
| December 31, | June 30, 2022 (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | (Unaudited) | |||||||||||||||
| Raw materials | $ 6,360 | $ 6,641 | $ 7,684 2321 6,954 | ||||||||||||||
| Work in process | 1,174 | 1,895 | 1,687 | ||||||||||||||
| Finished goods | 1,273 | 1,798 | 210 | ||||||||||||||
| $ 8,807 | $ 10,334 | $ 9,581 10,334 | |||||||||||||||
14
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
(4) Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, net, as of December 31, 2021 and 2020 and June 30, 2022 consist of the following:
December 31, |
June 30, 2022 20222022(Unaudited)_ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
2021 |
2020 |
(Unaudited)
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land | $ 995 | $ 995 |
$ 995 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Building and improvements | 5,449 | 5,434 |
5,449 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 11,557 | 10,811 |
11,906 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Office and computer equipment | 762 | 699 |
715 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18,763 | 17,939 |
19,065 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation | (11,594) | (10,214) |
(12,125) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ 7,169 | $ 7,725 |
$ 6,940 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 amounted to $1,380 and $1,099, respectively. Depreciation expense for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 amounted to $536 (unaudited) and $545 (unaudited), respectively.
(5) Income Taxes
Income tax (benefit) expense for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 attributable to loss from operations of the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment is presented below.
| Current | Deferred | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2021 | |||||||||||||||||
| Federal | $ — | $ — | $ — | ||||||||||||||
| State |
— —
|
— | — | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign | 52 | — | 52 | ||||||||||||||
| $ 52 | $ — | $ 52 | |||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| Federal | $ — | $ — | $ — | ||||||||||||||
| State | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign | 63 | — | 63 | ||||||||||||||
| $ 63 | $ — | $ 63 | |||||||||||||||
15
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
Income tax (benefit) expense for the six months ended June 30, 2022 (unaudited) and 2021 (unaudited) attributable to loss from operations of the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment is presented below.
| Current | Deferred | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Six months ended June 30, 2022 | |||||||||||||||||
| Federal | $ — | $ — | $ — | ||||||||||||||
| State |
— —
|
— | — | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign | 25 | — | 25 | ||||||||||||||
| $ 25 | $ — | $ 25 | |||||||||||||||
| Six months ended June 30, 2021 | |||||||||||||||||
| Federal | $ — | $ — | $ — | ||||||||||||||
| State | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign | 25 | — | 25 | ||||||||||||||
| $ 25 | $ — | $ 25 | |||||||||||||||
Actual income tax (benefit) expense differs from the “expected” income tax (benefit) expense computed by applying the United States Federal statutory income tax rate of 21% for all periods to loss before tax (benefit) expense due to state income tax benefits and federal research and development credits offset by the impact of uncertain tax positions and change in valuation allowance.
Deferred tax assets primarily consist of operating loss carryforwards, capitalized research and development costs, research and development tax credit carryforwards and inventory valuation reserves.
In assessing the realizability of its net deferred tax assets, management considered whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, management concluded that a net increase of $1,577 and $660, respectively, of the valuation allowance was appropriate. The change was the result of an increase in tax credits, net operating loss balances, and property and equipment differences due to depreciation. As part of management’s analysis, they evaluated, among other factors, its recent history of generating tax losses and its near-term forecasts of future taxable income or losses.
As of December 31, 2021, the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment has federal and state tax loss carryforwards of approximately $5,859 and $5,675, respectively. The federal loss carryforward has no expiration date. The state losses expire through the year 2041. As of December 31, 2021, the Segment had federal research and development tax credit carry-forwards in the amount of $500 that expire in years 2028 through 2041.
The net operating loss carry-forwards as well as the research and development credits generated hold no future benefit to the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment as they are not transferable assets. These tax attributes will remain with the Company.
The KVH Inertial Navigation Segment establishes reserves for uncertain tax positions based on management’s assessment of exposure associated with tax deductions, permanent tax differences, and tax credits. The tax reserves are analyzed periodically and adjustments are made as events occur that warrant adjustment to the reserve. The KVH Inertial Navigation Segment's policy is to recognize interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as a component of income tax expense.
The aggregate changes in the total gross amount of unrecognized tax benefits related to the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment are as follows:
16
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits as of January 1 | $ 433 233 | $ 370 269 | |||||||||
| Gross decrease in unrecognized tax benefits - prior year tax positions | — | — | |||||||||
| Lapse of statute of limitations | — | — | |||||||||
| Interest and penalties | 52 | 63 | |||||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31 | $ 485 485 | $ 433 433 | |||||||||
The IN Segment recorded interest and penalties of $52 and $63 in its statements of operations and changes in net parent investment for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. Total accrued interest and penalties related to tax positions taken on our tax returns and included in liability for uncertain tax positions was approximately $216 and $164 as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Management estimates that it is unlikely that the balance of unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2021 would decrease in the next twelve months as a result of a lapse of statutes of limitation and settlements with taxing authorities.
6) Business and Credit Concentrations
As of December 31, 2021, three customers accounted for approximately 53% of accounts receivable. As of December 31, 2020, two customers accounted for approximately 59% of accounts receivable, with one individual customer accounting for 44% thereof. As of June 30, 2022, three customers (unaudited) accounted for approximately 48% (unaudited) of accounts receivable.
Two customers accounted for approximately 27% and 33% of the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment’s net sales for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. For the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 two customers (unaudited) accounted for approximately 34% (unaudited) and 31% (unaudited), respectively, of net sales.
Certain components from third parties used in the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment’s products are procured from single sources of supply. The failure of a supplier, including a subcontractor, to deliver on schedule could delay or interrupt the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment’s delivery of products and thereby materially adversely affect revenues and operating results.
(7) Legal Matters
In the ordinary course of business, KVH Industries, Inc. is a party to inquiries, legal proceedings and claims including, from time to time, disagreements with vendors and customers. KVH Industries, Inc. is not a party to any lawsuit or proceeding that, in management's opinion, is likely to materially harm the inertial navigation business, its results of operations, its financial condition, or its cash flows.
(8) Commitments and Contingencies
In the normal course of business, the Company enters into unconditional purchase order obligations with its suppliers for inventory and other operational purchases. Outstanding and unconditional purchase order obligations for the KVH Inertial Navigation Segment were $5,959 as of December 31, 2021, which the Company expects to fulfill in 2022.
The KVH Inertial Navigation Segment did not have any off-balance sheet commitments, guarantees, or standby repurchase obligations as of December 31, 2021.
17
KVH INERTIAL NAVIGATION SEGMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
(in thousands)
(9) Subsequent Events
Management has evaluated subsequent events through October 25, 2022, the date that the accompanying financial statements were available to be issued and noted the following event that required disclosure:
On August 9, 2022, KVH Industries, Inc. entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement with EMCORE Corporation to sell to EMCORE the inertial navigation business for gross proceeds of $55,000, less specified deductions and a holdback of $1,000 and subject to a working capital adjustment. The sale was completed simultaneously with the execution and delivery of the Asset Purchase Agreement.
18